Shape correction, breast augmentation is one of the most popular plastic surgery procedures. With the help of a mammogram, you can correct congenital or acquired defects of the breast, restoring its volume and elasticity after childbirth and breastfeeding. Surgery done properly will help a woman become more attractive, more confident.
Indications for surgery
- Going down and reducing the elasticity of the mammary glands (mastoptosis).
- Increase breast volume while maintaining its sound and position (colon pathology).
- Decreased mammary glands after lactation.
- Small breast size (micromastia).
- Enlargement of breast volume in men (gynecomastia).
Types of breast plastic surgery
- Enlarged breast reconstruction(cosmetic cosmetology) - breast augmentation, correcting its shape using implants. It is used after childbirth, lactation, with congenital asymmetry.
- Reduce mammary gland shaping- Reduce bust size when having breast cancer (mastoptosis) or macroscopic disease.
- Mastopexy- breast augmentation. It is indicated for breast tumor, if the volume of the breast meets the requirements for surgery.
Endocrine of the mammary gland
The operation involves the installation of silicone prostheses (implants) into the mammary glands. The selection of incision site is suitable for the pregnant woman. The implant is placed under the pectoral muscle, and if the volume of the breast allows, between the muscle and the mammary gland. The incision is sutured, no drainage is required. Enlarged nipples and areola after surgery.
Breast implants
Silicone or polyurethane adhesives adjust the volume and shape of the bust, creating the feel of natural body tissues.
The life of the implants exceeds 15 years, after which they are recommended to be replaced.

The products differ in several indicators:
- Filler: adhesive gel or saline (sodium chloride). The composition of the gel is more elastic, homogeneous, light, but dangerous to the body if leaked. Saline solution is safer, softer, cheaper. Negative properties - gurgling when moving, prone to leaks.
- Texture: coarse (textured) or smooth. Implants have a more stable texture, but folds in the skin can appear due to the friction of body tissues against their surface. The disadvantage of plain dentures is the possibility of displacement.
- Shape: anatomical or round. The former looks more natural, while the latter retains the symmetry and shape of the breast even when displaced.
Reduce mammary gland shaping
When performing this type of surgery, fat tissue and breast tissue are partially removed, their size changes and a new shape is given.
Removing excess tissue reduces the chance of cancer.
Breast reduction surgery options:
- Liposuction. The method is considered conservative and leaves no seams. Designed to minimize breast with mild gynecomastia.
- Short seam (vertical). A popular method in which the breast maintains its natural shape and the nipple is sensitive. The surgery takes little time and the complication rate is low.
- Cut a T shape (anchor). Classic method, used for large amounts of tissue to be removed. Its downside is the recovery time, large scars.
- Amputation with nipple transfer. It is used for very large breasts. This method carries a high risk of damaging the mammary glands, making the nipples less sensitive and making it impossible to breastfeed.
Mastopexy
Breast augmentation without implants can be done in a number of ways:
- Vertical is used for mastoid level 1-2, seams are barely visible, lasting aesthetic effect. This method is not effective for cases of 3rd and 4th degree hypoplasia.
- Anchor mastopexy gives good results for ptosis of any degree of complexity. Its disadvantages include longer recovery time, noticeable stitches, increased risk of breast tissue damage.
- Periareolar mastopexy is the removal of a small section of skin around the areola. It is indicated for pseudopathy, for other forms of sagging of the bust it is ineffective.
Stages of Operation
For excellent cosmetic surgery results, high-quality medical care at all 3 stages is critical. The waiting period lasts 1-2 weeks. The actual surgical intervention takes from 1 to 4 hours.
Full recovery occurs within 1. 5 months.
Preparing for breast reconstruction

This operation is carried out no earlier than a year after the end of lactation. 2 weeks before surgery, hormonal contraceptives, aspirin and preparations containing salicylates should not be used.
You should stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
To prepare, research must necessarily be carried out:
- general blood and biochemical tests;
- ECG;
- blood test for anticoagulants (coagulogram);
- Breast ultrasound;
- General urinalysis
- HIV and hepatitis virus testing.
Surgical intervention process
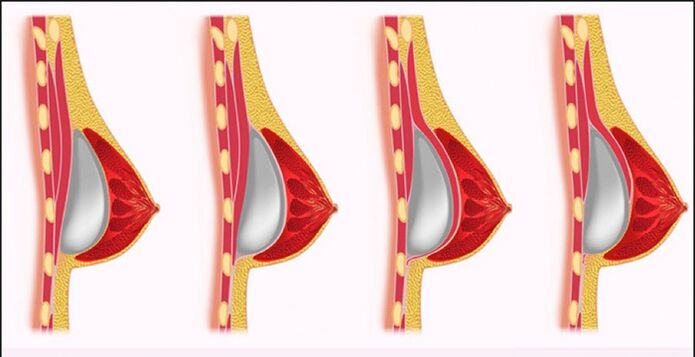
Breast augmentation surgery is performed under general anesthesia. A special type is the expansion turbocharger. It is used to increase the volume of the breast when there is a lack of native tissue and large implant sizes. The procedure is carried out in 2 stages. First, an expander is installed to gradually stretch the breast tissue over 1. 5–2 months.
When the desired size is reached, an endometriosis will be placed into the breast.
Surgical methods:
- Through the submammary fold (underlying gland access). Safe breast augmentation. The scar caused by an incision 4-5 cm long disappears over time under the slightly lowered breast. Difficulty accessing micromastia in thin girls.
- An incision around or along the lower arch of the areola (periareolar approach). Advantages - the surgical scar is barely visible. For patients planning to breastfeed, this method is not recommended due to the high risk of breast damage.
- Endoscopic buttock augmentation through the armpit. High-tech equipment helps the implant installation process without damaging blood vessels and nerve fibers. A 3-4 cm long incision is made in the armpit area, after which the scar is naturally concealed. There is a limit on the volume of the implant - up to 400 ml.
- Endoscopic approach through the umbilicus. This method is rarely used because the entry point is too far from the surgical site, and it is difficult to form a "pocket" for the restoration.
Rehabilitation after breast reconstruction surgery
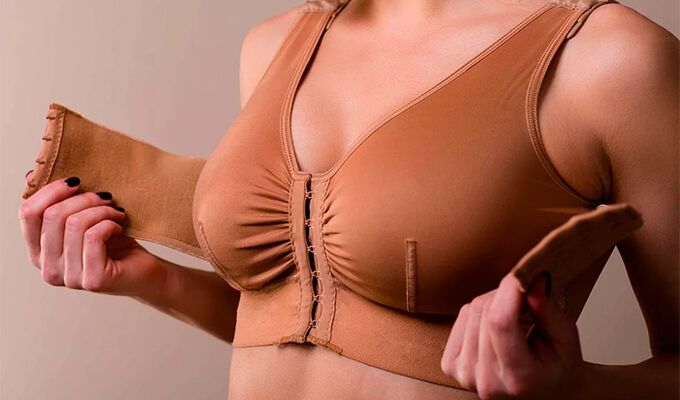

If the operation goes on without complications, the patient will be hospitalized for 3 days. After discharge, it is necessary to attend the tape. Moderate pain in the area of intervention occurring during the first few days is considered natural. The sensation of skin tightening may be due to post-operative edema, which should subside after about 5-7 days.
After 4-6 weeks, the breasts sag a bit, look more natural, and capsules form around the implants.
Successful recovery rule:
- No shoulders, no weight lifting.
- Do not go to fitness clubs, swimming pools, saunas, baths.
- Sleep on your back.
- Don't raise your hand.
- After breast augmentation, be sure to wear compression clothing.
Possible complications
- Capsule contract. The body forms a sheath that surrounds the intracellular matrix, which can lead to its displacement, violation of the symmetry of the mammary glands and hardening of them.
- Infection. Infection occurs during the operation due to a violation of the rules of asepsis or after non-compliance with the standards of antiseptic care. The specific risk period is 1 week after the operation.
- Keloid scars, hypertrophic scars. They appear if the body is inclined to form them. The formations look like dense ridges that protrude from the surface of the skin and damage the shape of the breast.
- Accumulation of blood, serous fluid (hematoma, serum) and as a result darkening of the skin. It occurs when blood vessels or lymph vessels are damaged during surgery or during recovery. Complications appear due to less blood clotting, sharply increased blood pressure, incorrect size of the intracellular.
- Decrease or loss of sensitivity of nipples and areola. Usually occurs when the mammary gland is reduced with reduced mammography due to nerve damage.
- Implant rupture. It occurs because of the thin crust, which is often found in cheap prosthetics. Salt fillers are easily absorbed by the body without harm. Damage to the adherent intracellular matrix is not always visible, but it is very dangerous if the silicone adheres to the tissues of the body.
Breastfeeding after surgery

The safest operation is through an incision in the armpit (transcapillary) or under the breast (lower gland).
About a year after surgery, breastfeeding is allowed.
Lactation problems can occur in the following situations:
- Endocrine is placed so that it compresses the mammary glands, reducing the volume of milk they secrete.
- A cut along the areola is more likely to damage the nerves around the nipple.
- Decreased plasticity, associated with a reduction in breast size, disrupts the milk ducts, blocking their functions.
In which cases is breast plastic surgery contraindicated?
- Cardiovascular diseases, varicose veins (thrombophlebitis).
- Severe forms of mastoid disease.
- Cancer.
- Blood clotting disorders, diabetes.
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza).
- Nervous and mental disorders.
- Pregnancy, breastfeeding.
- Age under 18.
Advantages and disadvantages of breast reconstruction surgery

Advantages of plastic breast correction:
- Apply modern interventions.
- Correction of congenital and acquired defects of the mammary gland.
- The cosmetic effect is long-lasting and obvious.
- Short terms of operation.
- The ability to choose the shape and material of the endoprosthes at will.
- Preserve lactation.
Possible disadvantages include:
- Skin marks from incisions - stitches, scars (unless special absorbent materials are used).
- Risk of complications (infection, breast deformity, bleeding).
- The need to replace endoprosthes every 10-15 years.
- The cost of breast reconstruction surgery is high.
- The need for general anesthesia.
- Pain in the first few days after surgery.
- The need to constantly wear compression underwear.
- A long period of recovery (from several months to a year) with the refusal of sports, physical activity, pregnancy, lactation.




























